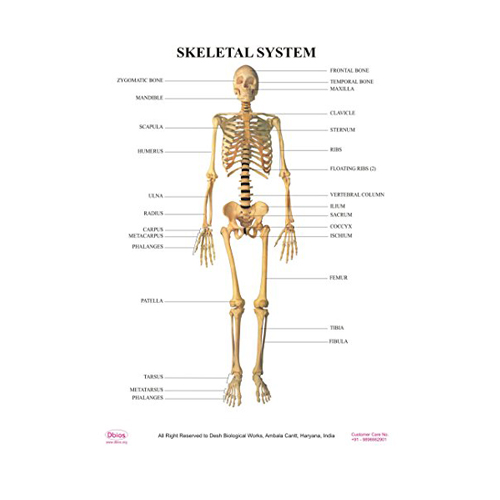
Skeletal System
Skeletal system is the system of bones, associated cartilages and joints
of human body. Together these structures form the human skeleton. Skeleton can be defined as
the hard framework of human body around which the entire body is built. Almost all the hard parts
of human body are components of human skeletal system. Joints are very important because
they make the hard and rigid skeleton allow different types of movements at different locations. If
the skeleton were without joints, no movement would have taken place and the significance of
human body; no more than a stone.
Components of Human Skeleton: • Bones • Cartilages • Joints
Functions of human skeleton: Human skeleton performs some important functions that are
necessary for survival of human beings.
Strength, support and shape: It gives strength, support and shape to the body. Without a
hard and rigid skeletal system, human body cannot stand
upright, and it will become just a ag of soft tissues without
any proper shape
Protection of delicate organs: In areas like the rib cage and skull, the skeleton protects inner
soft but vital organs like heart and brain from external shocks.
Any damage to these organs can prove fatal, therefore
protective function of skeleton is very important
Leverage for movements: Bones of the human skeleton in all parts of body provide
attachment to the muscles. These muscles provide motor
power for producing movements of body parts. In these
movements the parts of skeleton acts like levers of different
types thus producing movements according to the needs of
the human body.
Production of red blood cells: Bones like the sternum, and heads of tibia have hemopoeitic
activity (blood cells production). These are the sites of
production of new blood cells
| Cat. No. | ||
| 4222.2008.01 |